Welcome to Whiteboard Wednesdays, our new learning series where Coveo experts teach you how to build great search experiences.
Episode 1 dives into exposing your external content in a secure fashion inside another application like Slack. Follow along with Wim Nijmeijer, technical evangelist in the Coveo R&D Department.
Use Case
Often, people want to search their external content stored in places like Jira, Confluence, Sharepoint Online from within an application like Slack. Slack offers integration with custom applications, but getting content from multiple sources can be a burden. That is where Coveo comes in. Coveo already has connectors to index the content. During indexing, document-level security is also stored, which makes it possible to only show the results which a specific end-user is allowed to see.
Using the Coveo Search API, content can be accessed from within any application. Tracking user behavior is an important aspect for Machine Learning and Search Analytics, therefore the application a user is searching from must perform the necessary Analytics API calls to measure it.
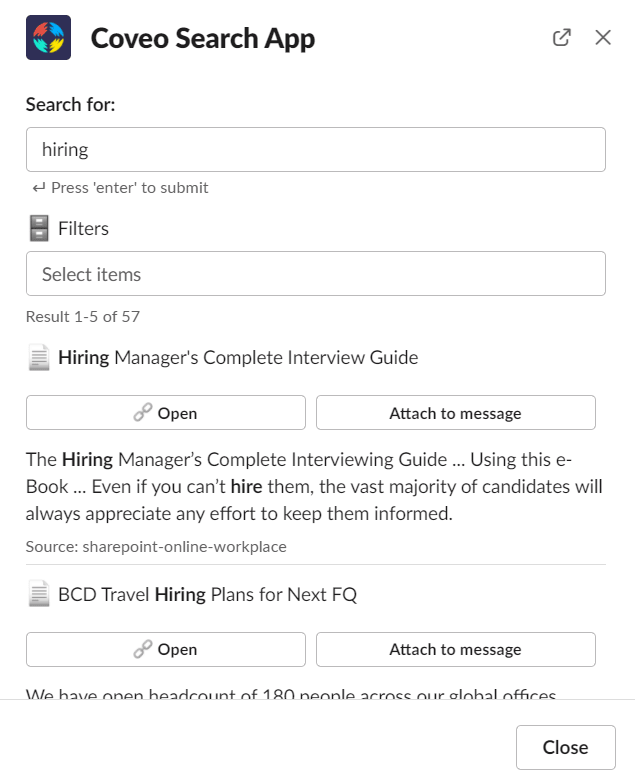
Integration Requirements
- Results shown from Coveo must be security trimmed
- Sent proper Analytics events to the Analytics API (submit and click events)
- Provide Analytics context from which channel the search was coming from
- Use commands, shortcuts, and modal windows within Slack
- Code github
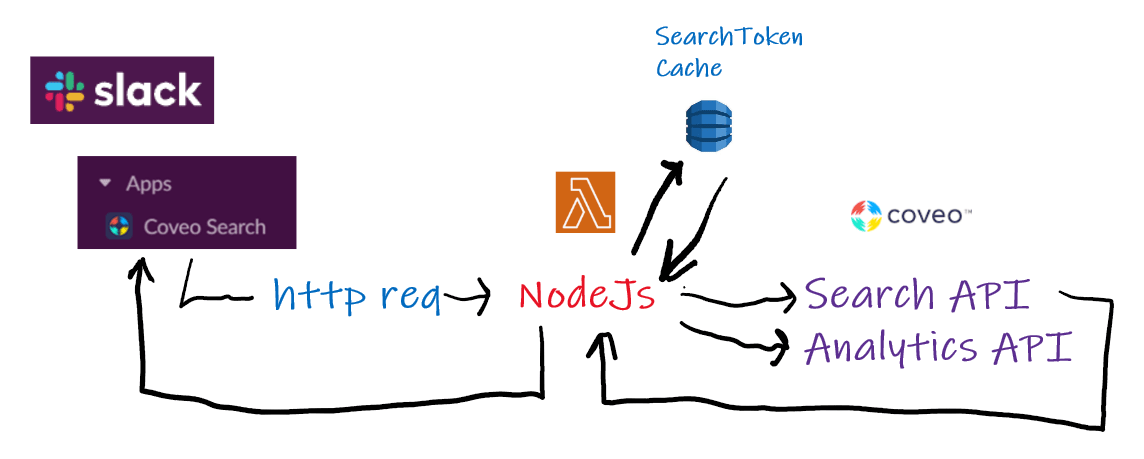
Architecture
The Slack Application is installed inside the Slack environment. The Slack Application communicates through http requests with our Node.js application. The Node.js application is hosted on an Amazon AWS Lambda function, which is exposed using the Amazon API Gateway. Our Lambda function communicates with an Amazon DynamoDB for our searchToken cache. Executes searches to the Coveo Search API and writes analytics data using the Coveo Analytics API.
Security?!
In the requirements, it’s very clear that security is a priority. Only results allowed for the current user should be shown. Most Coveo connectors support document-level security. This means the security of the source system is replicated for every document inside the Coveo index. After building the security cache, the Coveo Platform knows exactly what your end-users’ access rights are.
To get a Search API token, we first need to call the /token endpoint of the search API using an Impersonation API key. The code getNewSearchToken first checks if a token is available in the DynamoDB table. If not it will execute a /token call against the Search API. To obtain this token an impersonation API key is used.
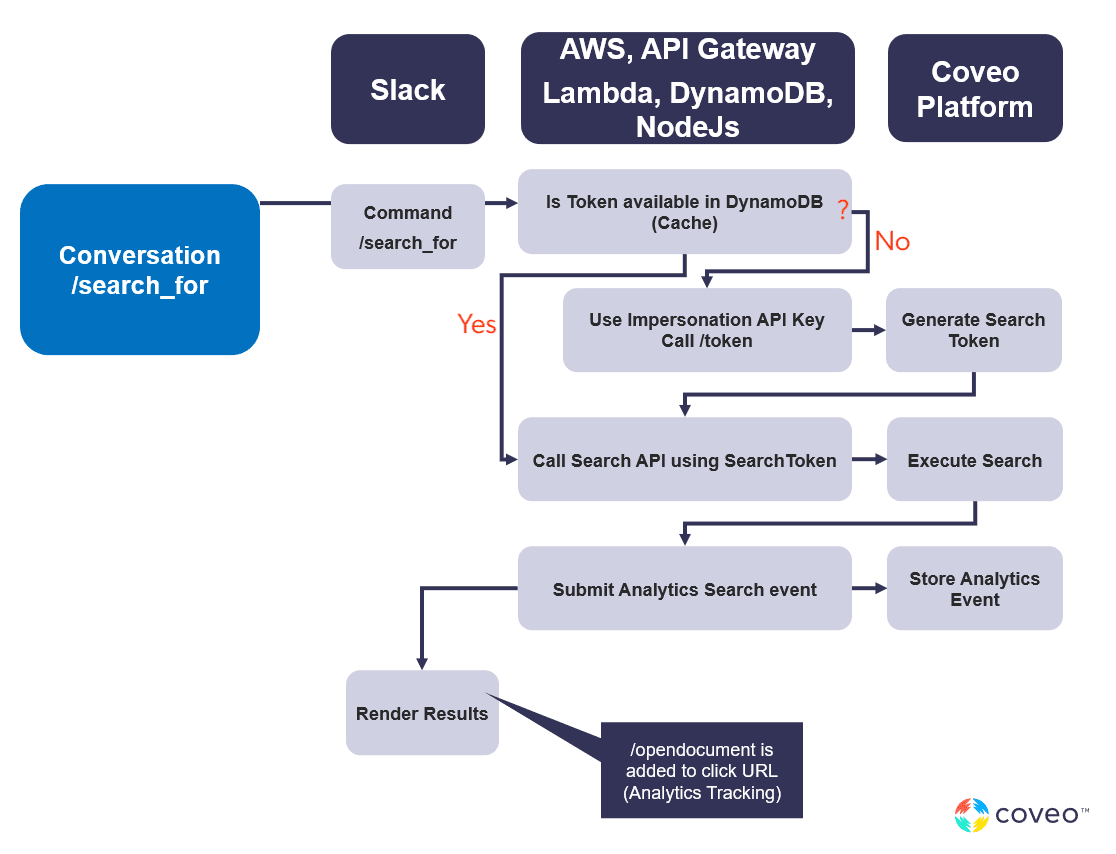
The token returned by the Search API is then used to execute search queries. The API key contains the current userId, based on that the security trimming of the search results is performed.
To have a single instance covering multiple clients, add the following URL parameters to all your Slack URLs.
| Name | Contents | Example |
| org | The Name of the Coveo Organization | workplcedem |
| apiKey | The Coveo API Key with Impersonation privileges (see above). | sdfa1234-2341234 |
Making it Work
Set Up Coveo Platform
The first thing we need to set up is the API key, used for the impersonation. Store this key in a safe environment and do not expose it! In the provided example, it is stored in the AWS application in the .env file. You could also add it to all of your Slack URLs by using the query parameter apiKey=YOUR_KEY. Using the impersonation API key creates a search token, which is used for searches and storing analytics data.
We also need a dimension to store our channel data. This channel data can then be used in analytic reports.
Add the dimension called channel and map it to: c_context_channel, and check the boxes for Search and Click events.
Create Amazon DynamoDB table
Now that our Coveo Platform is set up, an Amazon DynamoDB table must be created. This table is used to store the cache for the generated search tokens.
aws dynamodb create-table ^
--attribute-definitions ^
AttributeName=user,AttributeType=S ^
--key-schema ^
AttributeName=user,KeyType=HASH ^
--table-name awsSlackCache ^
--provisioned-throughput ^
ReadCapacityUnits=1,WriteCapacityUnits=1 ^Create the Slack Application
A Slack application must be created and configured. Most important information we need from this configuration is the Signing Secret and the Bot User OAuth Token. This is needed for our Node.js application.
Create the Node.js Application
The Node.js application needs to react to the requests sent by Slack.
Commands
In the application you need to define:
app.command('/search_for', async ({ command, ack, say, context, respond, payload }) => {which is then mapped to the Slack application in the slash commands.
The /search_for command simply executes a search (first requesting a search token), and responds back to Slack by providing a list of results.
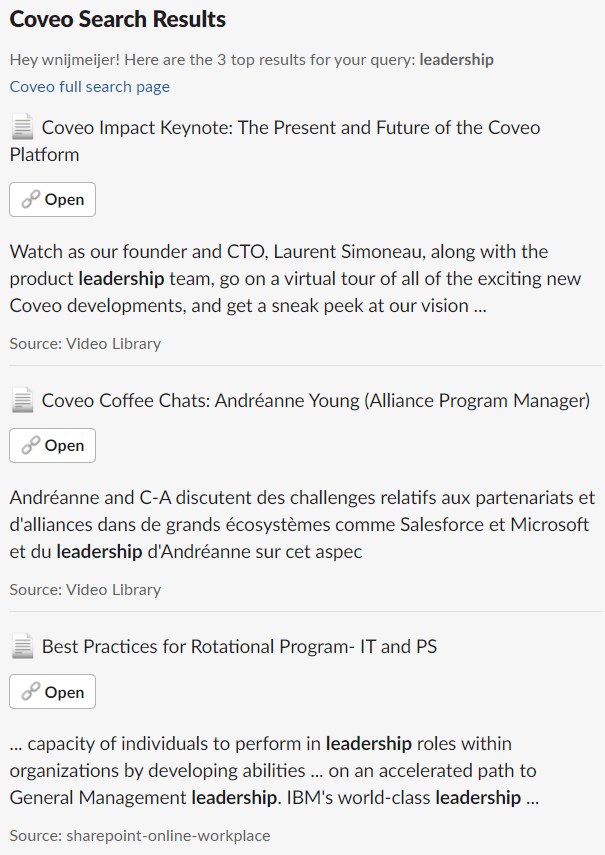
The /search_for_modal

Every time you update the search box content, or select a facet, the view of the modal window is updated.
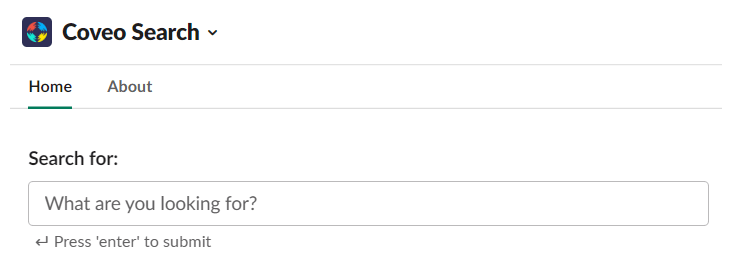
Home Tab
The modal window is the same as when invoked from the Home tab of the application.
Shortcuts
Reacting to shortcuts is defined differently. You must use:
app.shortcut({ callback_id: /.*short-modal/, type: 'message_action' }, async ({ shortcut, ack, say, body, client, context, respond }) => {The callback_id is configured in the URL when creating the shortcut in the Slack application.
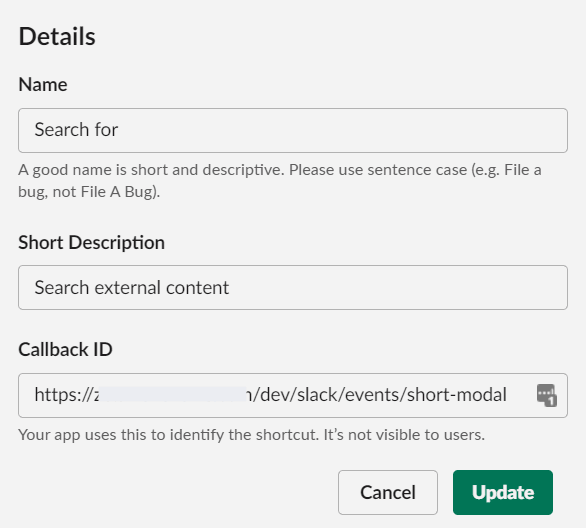
The callback_id is the URL pointing to Amazon AWS + /short-modal.
Actions
Any interaction (button click, search query, etc.) that you want to capture analytics for must first be configured as a content block with an action_id:
addMessageObj = {
"type": "actions",
"elements": [
{
"type": "button",
"text": {
"type": "plain_text",
"text": "Attach to message",
"emoji": true
},
"value": ClickUri,
"action_id": "attachToMessage"
}
]
}The action_id is then cached like:
app.action('attachToMessage', async ({ action, ack, body, client, context, respond }) => {Respond and Report Analytic Events for the Coveo Platform
When a search is being executed, an Analytics event must be sent to the Coveo Platform. In the Node.js application, we use the submitAnalyticsSearch method. This will send the current search information. The Search API token already contains the user information, so that is also logged in the Analytics.
If that should be avoided, you could simply specify "anonymous": true in the Analytics calls.
Important here is that the searchQueryUid is the same as the one retrieved from the Search API. The searchQueryUid is also stored when opening documents. Based on that, the Machine Learning can relate the two events together.
The second event we need to send is when end-users open the document. A /click event must be sent. Important, because the Machine Learning algorithms use this to report ‘successful’ searches. Using submitAnalyticsOpen will send the event. This event should only be sent when end-users click on the actual document. Therefore, we have constructed an open button to open documents.
Deploy the Node.js on Amazon AWS
Use npx serverless offline --noPrependStageInUrl for local development (and use ngrok to expose the URL). Use npx serverless deploy to deploy to Amazon.
Assign the Proper Security Policy to Your Lambda Execution Role
Make sure you add Read/Write access to your Lambda execution role on the created DynamoDB table.
Configure the Slack App
URL is the AWS URL of the API gateway.
- Open your Slack App Settings.
- Navigate to Interactivity & Shortcuts.
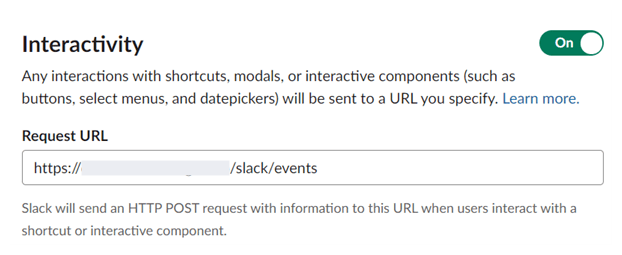
- Enable
Interactivity. - In the
Request URL, enter:URL/slack/events.
- In the
Shortcuts, add a new shortcut and enter:

For the Callback ID, enter: URL/slack/events/short-modal
- Navigate to
slash commands - Create a new command, and enter:
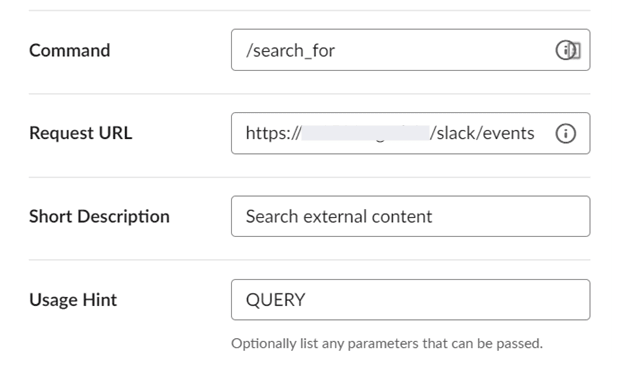
For the Request URLURL/slack/events
- Create a new command, and enter:
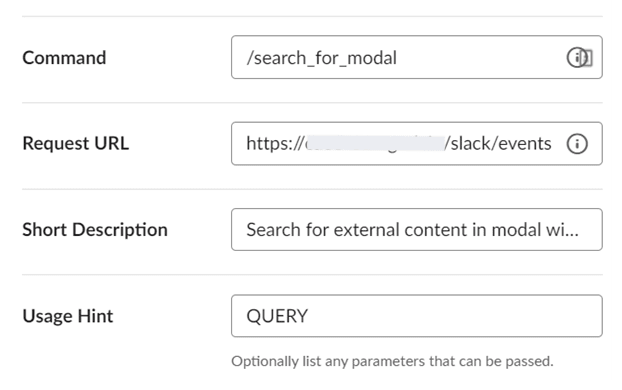
For the Request URL, enter: URL/slack/events
- Navigate to
Event Subscriptions. - Enable events subscriptions.
- Enter the same request URL as in step 3.
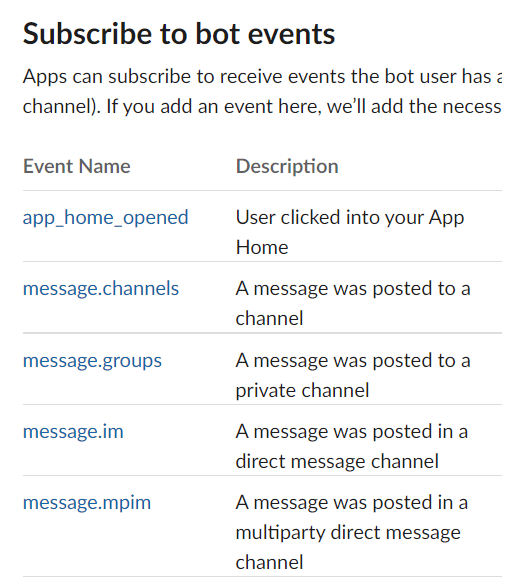
- Enable the
Subscribe to Bot eventsas follows:
Use it
Use Slack commands:
/search_forto search for text/search_for_modalto search for text with a modal screen. You can use facets to refine your search.
Use shortcuts:
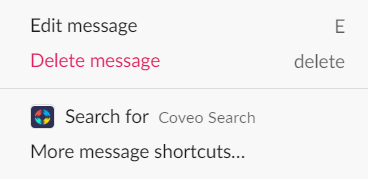
Use Home tab:
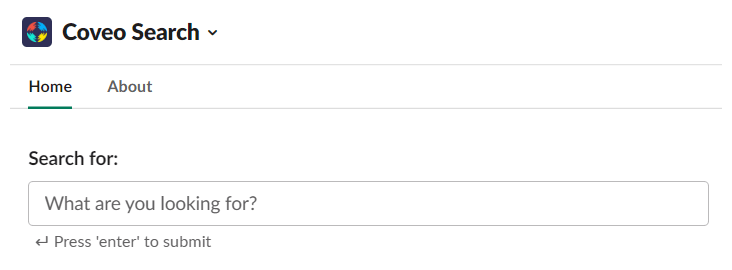
Dig Deeper
Interested in trying Coveo out for yourself and integrating ai search in Slack? Give our trial a spin.


