Generative AI (GenAI) is a branch of artificial intelligence that can create new content (e.g., text, images, code, etc.) based on existing data and models. It’s gained popularity in recent years, thanks to the development of powerful large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-3 and GPT-4.
But what does GenAI mean for ecommerce? How can it enhance the online shopping experience for both retailers and customers? And what are the risks involved in adopting this technology?
We turned to our colleague Simon Langevin, who heads up Product for Commerce here at Coveo and has 10 years in the IT world. As one who has to separate hype from reality and turn it into a product, his job is to be grounded in pragmatism. So, what’s really possible in the near future and beyond? And at what cost?
Here are some of the key insights he shared with us.

GenAI Debunked: Ecommerce Risks and Misconceptions
Watching GenAI actually write answers conjures up all sorts of ecommerce use cases, especially related to search. But Langevin held up a caution flag. “It’s not a silver bullet that can solve all ecommerce problems,” he said emphatically. “There are many misconceptions and risks that leaders must address before implementing GenAI for ecommerce search.”
For starters, Langevin pointed out that GenAI cannot bypass or replace other technologies that are essential for ecommerce search features,such as semantics, catalog enrichment, image tagging, and synonyms. “Generative AI relies on these technologies to understand the context of queries and products, and to avoid errors or inconsistencies. What most people don’t realize is that GenAI is augmented by these technologies, and not the other way round.”
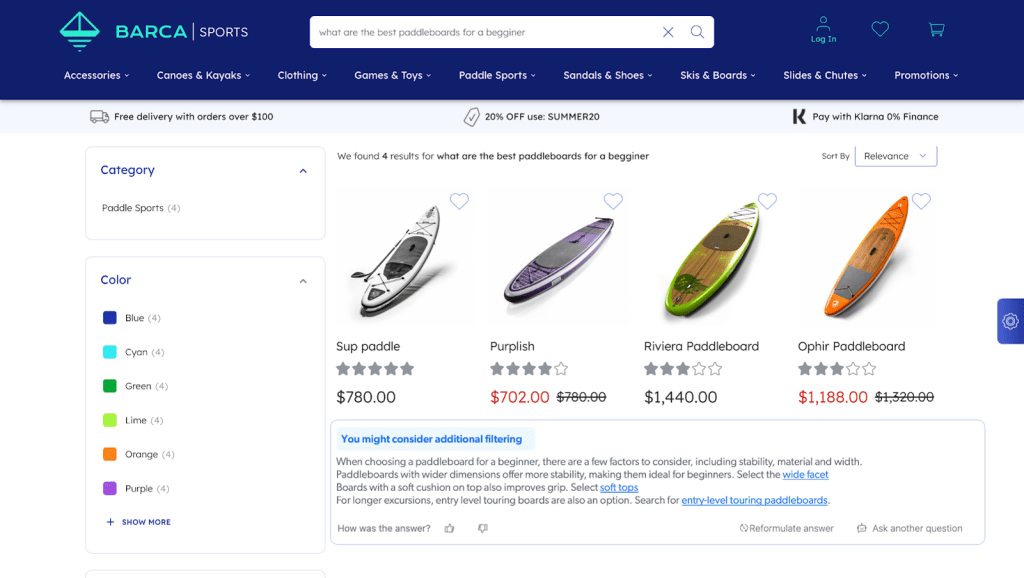
For instance, if a customer asks: “what’s the right paddle board for a beginner”, the LLM will understand the query and generate a response which usually contains critical attributes to look for, e.g. a wider, softer board, etc. However, there’s a chance that these product attributes will be wrong, and importantly, they will rarely match your own product catalog.
To combat this, you must use semantic technology, which is able to understand user intent from the content of a query. This helps GenAI create relationships between the attributes generated by GenAI (and its training data) and the content of your catalog.
“There are numerous use cases attributed to GenAI that would be better solved using other technologies,” he said. “For example, while some vendors promote GenAI as a solution for catalog enrichment, this use case could be addressed with better, and cheaper technologies. While GenAI could look at a particular product image or description and generate additional tags for the product, there’s a high likelihood this will result in hallucination.
“Instead, technologies like image tagging, or simply drawing inferences from other similar products, would probably do a better job, and at a lower cost.”
While Langevin believes that GenAI will become more cost effective with time, at the present, it continues to be costly and represents heavy processing for organizations. GenAI requires a lot of processing power and resources, therefore use cases must be analyzed carefully to ensure profitability.
Perhaps more importantly in the short term, however, is minimizing the risks for hallucinations and false or misleading information. Ecommerce leaders should be careful and selective about where and how they use GenAI. They should choose vendors with expertise in grounding GenAI on company data and catalogs.
GenAI Benefits in Ecommerce — Today
According to Langevin, GenAI can have a significant impact on ecommerce, mainly through providing solutions for product discovery and shopper education (aka, knowledge discovery).
For instance, a use case that has gained popularity is leveraging GenAI to summarize and present relevant knowledge —everything from blogs, articles, how-to guides, etc. — to educate customers about the products they’re looking for.
For example, if a shopper is searching for a paddle board for beginners, GenAI can generate a summary of the best practices, tips, and expert recommendations. It can then link them to the appropriate attributes in the catalog. This allows buyers to refine the scope of their product discovery journey. Similarly, in industries like grocery, GenAI can provide relevant recipes and link shoppers to additional cooking utensils they may need. And in more technical industries, GenAI can provide quick access to product guides and technical spec sheets that are critical to driving purchase, plus ensuring a successful post-purchase experience.
Using GenAI to support knowledge discovery is highly cost effective because it focuses on resolving specific types of queries, such as ‘What is”, “How do I”, “Why should I”, etc. Furthermore, it has the potential to differentiate ecommerce brands from their competitors by showcasing their expertise and authority in their niche. This can be particularly impactful in B2B commerce scenarios, where, in addition to the actual buyers, there’s a range of customer profiles visiting your site, e.g. engineers, procurement, field service technicians, etc. And if, for instance, your content is able to support and educate an engineer, who then ends up choosing one of your components for their final design, you may have just secured an order worth millions.
“These use cases can positively impact ecommerce metrics such as conversion rates, average order value, customer satisfaction, and loyalty,” he said. Nevertheless, he highlights that this is all very recent and the volume required to achieve statistical significance has made it hard to prove the impact of GenAI so far.
Is GenAI Right Now, Right for You?
At this point you might be wondering, “is it really worth it for me to integrate GenAI into my ecommerce strategy?”
It depends.
Langevin’s viewpoint is, if you’re competing with Amazon, or if you sell thousands of products across thousands of categories, GenAI might not be for you (at least not in product discovery). However, if you’re a brand that people regard as a source of information and insights (as well as products), then GenAI can be more relevant.
“If your brand serves a niche segment (e.g., river rafting) and sells a number of products for that niche, GenAI may offer an opportunity for differentiation,” he explained. “You’ll be able to showcase your expertise on that topic and gain customers’ trust, which will eventually bring them to your products.”
In other words,the current state of GenAI is ideal for specialty brands with enough content for product discovery. Or B2B scenarios where the information about your products is a central element to the purchase journey.
GenAI Implementation: Do’s and Don’ts
Finally, Langevin shared some best practices for ecommerce leaders who want to implement GenAI in their ecommerce ecosystem, mainly:
- DO start with a clear business objective and use case for GenAI. Identify where GenAI can add value and improve the customer experience.
- DON’T believe GenAI will just magically solve all the ecommerce problems you have today. A lot of LLM magic sits on top of other technologies, e.g., semantics and catalog enrichment.
- DO choose a vendor that can provide a proven track record of successful implementation of GenAI for ecommerce search. Seek vendors who can ground context on your data and catalog (i.e. ensure secure, accurate and consistent personalized answers), avoid hallucination or irrelevant content, and most importantly help you measure the economic impact of GenAI.
- DON’T skip over security measures. There can be lots of privacy issues with GenAI — this can be mitigated with the right vendor.
- DO test and experiment with different scenarios and segments of customers. Use A/B testing or other methods to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of GenAI compared to other approaches.
Need to know more?
GenAI and its applications for ecommerce are rapidly evolving, and eventually may transform ecommerce as we know it.
Watch Langevin deep-dive into these topics in our webinar: GenAI for Ecommerce and understand how to use this technology in your business in a way that truly maximizes profitability and minimizes risk.