Based on the enormous interest in OpenAI’s ChatGPT, artificial intelligence (AI) is experiencing a breakthrough moment with Generative AI.
Like other forms of AI, Generative AI learns how to take actions from data.
With its ability to learn and generate new content, Generative AI promises to help businesses improve efficiency, reducing costs. In the long run, this may lead to freeing up resources to focus on core business activities.
The excitement around Generative AI has reached ecommerce as well. Generative AI is tantalizing people with what it could ultimately mean to shoppers and ecommerce leaders. And with 94% of respondents to our annual Ecommerce Relevance Report saying they expect online to be as good or better than in-person, it could be the bridge to tie these two worlds together.
What Is Generative AI in Ecommerce?
Generative AI is a type of AI technology that can produce content, including text, imagery, audio, and synthetic data.
The rapid pace of AI development and public release of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have attracted widespread interest. Yet ChatGPT is but one language transformer model. While not exactly the first, Google’s BERT has had a tremendous impact, as testified by the over 70,000 citations received so far (based on Google Scholar). Bard is Google’s chat function, which uses BERT.
You might notice the final letter for both models is T – which stands for Transformer. Transformer models allow you to generate human-like text that underpins natural language understanding.

These have been used in ecommerce as well. In fact, leading ecommerce tech companies have been using and fine-tuning Transformer-based models for years.
ChatGPT uses Transformer architecture to generate text that is coherent and contextually appropriate based on received input. It’s one example of how Generative AI can create sophisticated and engaging content in a variety of contexts.
What truly makes ChatGPT or Bard unique is that they are free and publicly available. They boast a user-friendly interface, and were trained with data sets that are larger than previous LLMs. ChatGPT has made Generative AI technology more tangible than ever before, as evidenced by its rapid uptake by the public.
Power Couple: Multimodal & Generative Models
Our post on Natural Language Processing (NLP) explains how chatbots leveraging AI capabilities are a vibrant area of research and innovation. But the latest trends in Generative AI are not just about language generation, but involve multimodal AI models.
Multimodal AI refers to AI that combines multiple data types (or modes) to create more accurate determinations, draw insightful conclusions, or make more precise predictions about real-world problems.
It means numerous data types are used in tandem to help AI better interpret context, something missing in earlier AI. OpenAI released a popular, multimodal large model in 2021. This learns visual concepts from natural language and can help with a number of tasks, from retrieval to classification.
Coveo agrees on the value of multimodal AI. And has introduced a domain-aware large model tailored to the fashion industry — FashionCLIP. Research shows that FashionCLIP outformed CLIP across relevant use cases and datasets.
Ecommerce companies can use vector representations of product images (produced by text-to-image models like FashionCLIP) to improve product search. As a result of these types of developments, leading ecommerce companies have been adopting multimodal models.
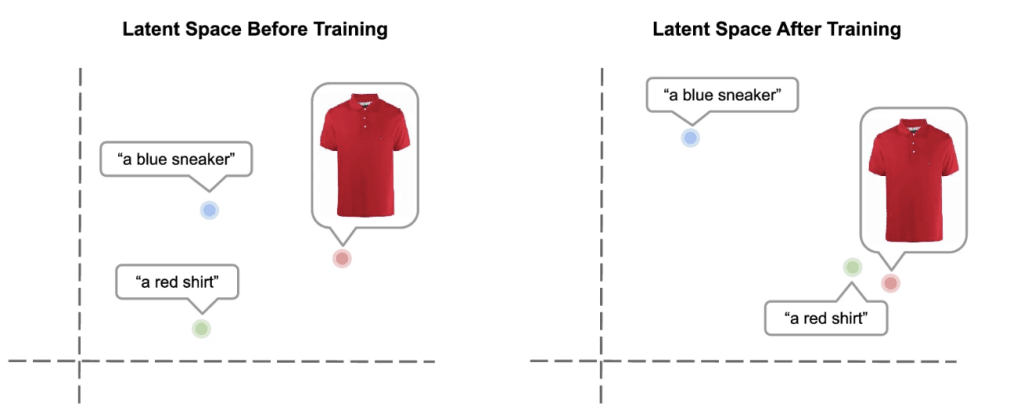
And now, multimodal AI has met up with Generative AI. Next-generation multimodal models, such as GPT-4, can ingest product images and product descriptions together. It can then extract a wide range of attributes from this data.
What Are Key Use Cases for Generative AI in Ecommerce?
The most natural application of Generative AI to ecommerce focuses on boosting CSAT with post-purchase self-service. It has the potential to significantly transform customer service by acting as a collaborative partner while in an ecommerce store.
One of the most common use cases for retailers has been the use of chatbots. A chatbot driven by Generative AIversus a traditional decision tree can help provide superior service — without needing a live human agent.
Importantly, Generative AI can be used to rapidly source answers from intricate documents and generate the most compelling answers. Imagine a customer has acquired a Speedbit device and now visits the Speedbit Blaze portal to find information on “how to track heart rate” with her new device.
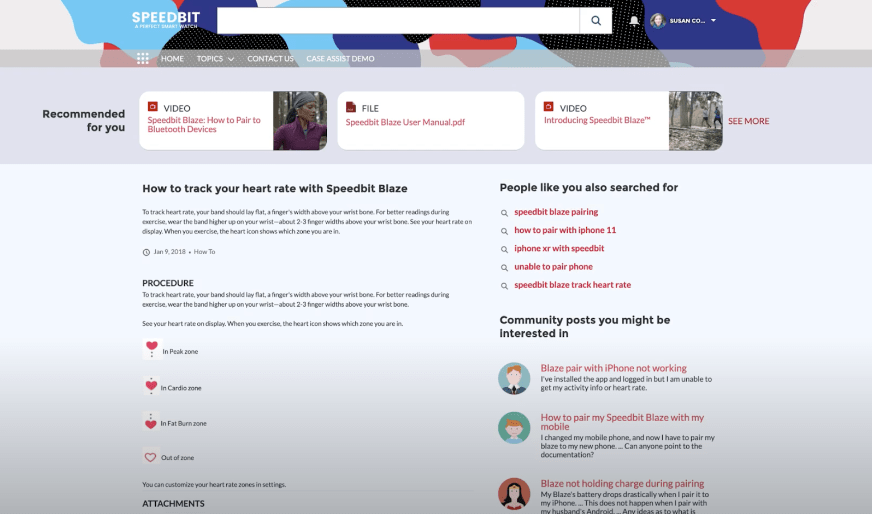
Leveraging Generative AI capabilities, it’s possible to easily generate an accurate answer, tailored completely to the user. Factual, up-to-date — complete with citations to the original documents.
Examples of Generative AI in Ecommerce
While post-purchase self-service is the prime example of an ecommerce use case, there are of course other applications. Some players have already incorporated Generative AI capabilities or have announced plans to do so.
For example, Shopify has integrated ChatGPT into its consumer-oriented Shop app, to be a virtual shopping assistant able to answer questions with relevant, helpful answers. Further, it will also offer some product recommendations based on your questions.
Others, like Newegg, are using AI to automate the review process for website product description content for all new marketplace product listings.
Expedia is an example of a company testing GenAI’s potential in ecommerce. They recently launched a ChatGPT interface.
Also Instacart recently announced their ChatGPT integration to further improve their search capabilities and support longer, conversational queries.
Amazon is also reportedly looking towards Generative AI to essentially bring ChatGPT-style technology to improve search, mirroring efforts by Google, Microsoft, and others.
And of course, there are tons of further opportunities and potential use cases. But an important factor to consider is that many of these applications are radically new and their commercial application is both unknown and untested.
Retailers know very well that ecommerce conversion rates are still low in 2023. So the last thing they would want is to just introduce a new UI experience altogether or new Generative AI capabilities. Be sure to carefully evaluate any new technology’s impact on the shopper experience — and the bottom line.
Generative AI Challenges to Consider in Ecommerce
Even more importantly, while Generative AI is impressive, there are further notable challenges when moving models to production in ecommerce. These range from quality assurance (“we’ll harm our brand and bottom line if end users see hallucinations”) to scalability (“the right balance of performance, latency and costs”).
More precisely, the market is in a hype phase, creating a lot of pressure to “announce something”. As we’ve seen, some companies are announcing integrations with generative AI applications (such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and other Generative AI tools and LLMs). But as exciting as GenAI applications in ecommerce can be, there is always room for grounding.
It is important to understand that the challenges and risks are far from trivial.
Avoiding Hallucinations in Ecommerce
Let us start by considering quality assurance and threats of hallucination. It is not news that LLMs are often wrong, and they are confident about it. So, Generative AI is impressive, but currently plagued by hallucinations and inaccuracies. In the context of ecommerce, factuality is indeed a critical concern. In particular, it is vital to respect inventory, store availability, and entitlements.
Here is an example from Bing GenAI on the query, “Best laptop for a student on a tight budget:”

This experience looks great. But has two issues:
- It hallucinates on the price; most of these computers are much more expensive
- It hallucinates on the content; in this case, the source being referred is an article that never mentioned Dell Inspiron 15
Other types of hallucinations a Generative AI in ecommerce might suffer from include:
- Misleading reviews: Customers may rely on fake or biased reviews when making purchasing decisions, leading to incorrect perceptions of a product’s quality or performance.
- Imaginary discounts: Retailers may create the impression of a discount by artificially inflating the original price or offering limited-time promotions that are not actually savings.
- Phantom inventory: Retailers may advertise products that are out of stock or no longer available, leading customers to believe they can purchase an item when they cannot.
There are ways to combine Generative AI capabilities and the knowledge base’s accuracy to mitigate these concerns, but more generally product discovery vendors have an important role to play in exercising due diligence to ensure the fit-for-purpose of models for specific tasks.
Partnering with a vendor known for its research and innovation efforts of course can help de-risk Generative AI initiatives.
Latency Is the Limit
Hallucinations aren’t the only threat to consider.
88% of online shoppers say they are less likely to return to a site following a subpar experience. While a number of factors can make for a less-than-ideal shopper experience, latency is key in ecommerce.
An Akamai study shows that every 100-millisecond delay in website load time can hurt conversion rates by 7%. Amazon found that a 100ms delay causes about a 1% drop in revenue. Amazon also found that loading 30 results instead of 10 delayed the page rendering by .5 seconds, causing a 20% drop in traffic.
In a world where nobody likes waiting, the last thing you want is to introduce new technologies that could negatively affect your UX by impacting latency.
Generative AI is still slower than a typical search request performed in less than a hundred milliseconds. Waiting for the prompt to provide a rich answer and then retrieving results may not lead to the best experience for shoppers as of today.
And while we are confident that smaller, more precise models – as well as continuous improvements of the technology will likely improve latency – we are still far from the expected speed of a typical search-powered shopping experience. So that will need to be kept in mind when designing the user interface.
Getting Ready for Generative AI in Ecommerce
As we’ve seen, Generative AI in ecommerce is such a thriving area of innovation that brings a lot of possibilities and can have a deep impact on product search & discovery. But at this point there are still a number of questions that need to be answered.
Ultimately the use cases that will gain momentum are those that excite the customer (by bringing the biggest benefit!) and those that can be cost-effectively supported by retailers.
Choosing to partner with a tech vendor that has a strong record of innovation and research in ML and NLP — that addresses the issues like trust and security head-on — is a solid way of de-risking Generative AI investments and efforts in ecommerce.
Dig Deeper
Learn more about Coveo’s history with LLM, ML, and NLP applications. Seize the opportunity to speak with an AI expert about your unique concerns.