A digitally accessible and inclusive workplace ensures that every employee, regardless of ability, can easily access the information they need to excel in their role.
Consider that 40% of people need digital accommodations of some sort to access information, but only 20% of digital touchpoints (websites, intranets, apps, etc.) are accessible to everyone. This access gap prevents a significant number of employees from obtaining the information they need to do their jobs.
True digital inclusion goes beyond supporting current employees. It means making sure your entire hiring process is accessible starting with the job descriptions you post and incorporating accessible training and onboarding strategies. Providing an equal opportunity for every qualified person to find, apply to, and be fairly considered for open positions, expands and diversifies your talent pool.
In this post, we’ll cover the essential information you need to create a digitally accessible workplace: including what this means, how AI plays a role in enabling disability inclusion, and what this means for businesses.
What are Reasonable Accommodations?
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, and this extends to the digital workplace. A reasonable accommodation, as defined by the U.S. Office of Disability Employment Policy, is:
“A modification or adjustment to a job, the work environment, or they way things are usually done during the hiring process that enable an individual with a disability to have an equal opportunity not only to get a job, but to successfully perform their job tasks to the same extent as people without disabilities.”
— Office of Disability Employment Policy
Reasonable accommodations incorporate physical changes, accessible/assistive technologies, accessible communications, and policy enhancements. Policy involves a whole-business approach.
It requires baking accessibility into your company culture by cultivating attitudinal awareness about workplace accessibility, educating employees and managers about disability discrimination, and creating a comprehensive disability employment policy.
In this context, equal access to digital content, tools, and technology is considered a reasonable accommodation for employees who have physical or cognitive disabilities. Let’s look at what that means.
Digital Accessibility in the Workplace
Digital accessibility, as defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), means that a website or other digital resource (e.g., apps, tools, technology) is accessible to people with disabilities.
Specifically, digital accessibility touches on the following five key elements, ensuring that people can:
- Perceive – Understand and interpret information presented on the web.
- Understand – Comprehend the content and functionality of websites and applications.
- Navigate – Move through web pages and interact with different elements.
- Interact – Engage with web content, forms, and other interactive features.
- Contribute – Participate in online activities and contribute their own content.
Web accessibility addresses any disability that may compromise access to digital content including visual, speech, physical, neurological, cognitive, and auditory disabilities.
As an employer, you’re responsible for ensuring that digital tools, information, and the ability to easily communicate are part of your Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) approach.
Making resources like internal intranets, websites, and technology accessible to disabled employees directly benefits your business and the people who work for you by connecting important information to the people who need it. This is a key area where AI-powered technologies can help.
We covered major workplace trends for 2024 back in January. We found that employees are increasingly dealing with rapid shifts in technology, customer expectations, and an influx of information from multiple sources. This can be overwhelming, particularly for those who may face additional barriers to accessing digital content.
Artificial intelligence has been an important driver in making information more accessible to employees, applicants, and new hires. Now, we’ll break down some specific use cases that cover how AI can improve digital workplace accessibility.
AI and Digital Accessibility in the Workplace
AI is being used to transform employee experience, improving accessibility and productivity in digital spaces. Coveo’s technology covers several important accessibility use cases that contribute to creating a digitally inclusive environment for disabled workers. We break these down, below.
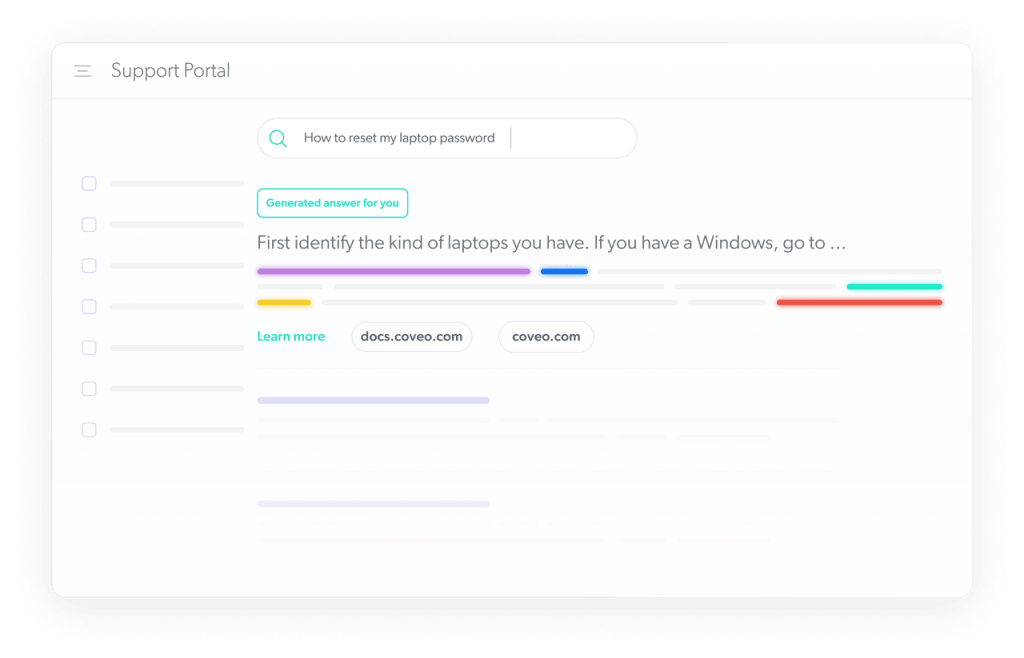
AI-powered search makes intranets more accessible
AI improves employee experience by helping your team find the information they need across corporate data repositories and applications. Coveo’s intelligent search engine uses 11 AI models, including query suggestions, content recommendations, smart snippets, and generative answering, to help knowledge workers find relevant information in a unified, intuitive way.
AI-enabled search is incredibly beneficial for employees with cognitive disabilities or neurodiversity since they may struggle with information overload or have difficulty navigating complex information architectures. It simplifies the process of locating relevant content.
AI customizes information retrieval
AI makes it possible to deliver role and task-specific information to employees based on their context and needs. This improves productivity by reducing time spent switching between different interfaces and databases (e.g., “context switching”) in an attempt to find the information they need. Personalization is also important for supporting workers at different stages of their careers (e.g. a new hire vs a seasoned employee).
Since AI can tailor the user experience and content to a user’s specific access needs, it improves technological accessibility by presenting information in alternative formats like simplified text, images, or audio.
AI keeps information relevant and current
Real-time access to information is important for all employees, particularly if they don’t have immediate access to a colleague or on-site database. By creating a unified index of your company’s knowledge base, you make information easily searchable and retrievable by AI-enabled unified search tools like Coveo. This gives employees access to up-to-date information in real-time even when they’re working from home or in the field.
For employees who use assistive technologies, outdated or incorrect information can create additional barriers. The ability to access real-time information across a company’s entire knowledge base, find related content quickly, and work from the most current resources provides a strong foundation for creating a digitally accessible work environment.
Conversational interfaces expand access to information
Generative AI is enhancing workplace experience by enabling more natural language interactions for employees. Employees can use voice or text search to ask questions and trust that the search engine “understands” the context and surfaces the most relevant results. For example, Coveo’s Relevance Generative Answering uses AI and ML to understand queries and pull tailored responses from various internal knowledge bases.
Conversational interfaces can be particularly useful for employees with visual impairment or mobility limitations. They allow those performing either on-site or remote work to access information without relying solely on visual cues or complex navigation.
More Ways AI Revolutionizes Workplace Accessibility
AI’s impact on workplace accessibility extends far beyond the examples we’ve already covered. Emerging technologies like AR and VR offer exciting opportunities for immersive employee experiences, although it’s true they also pose new access challenges. Here are a few more examples of how AI facilitates a digitally inclusive environment for all workers:
AI-powered speech-assistance
Tools that translate distorted speech patterns into fluent conversations help people better communicate. For example, they can process and interpret input from people with speech impairments and turn it into more natural-sounding text.
AI-fueled learning
Tools like braille tutor apps make education more accessible for visually impaired workers. They use optical character recognition to convert physical braille into digital text. Transcription tools record and transcribe in real-time, which is incredibly helpful to those with hearing impairments. It allows them to participate in meetings and calls and provides searchable transcripts for easy reference versus taking notes.
AI-enabled virtual assistants
Siri and Alexa can search the internet, check email, make phone calls, and even open documents. This makes digitally-intense jobs much easier to manage for disabled workers.
AI-automated workflows
Chatbots integrated into work apps can assist with tasks, while robotic process automation streamlines repetitive processes. These efficiency gains benefit everyone and can help reduce information overload by delegating repetitive tasks to the robots.
AI-enhanced readability and tone analysis
There are many AI-enabled writing and editing apps focused on improving the readability of written content. This helps people with learning differences like dyslexia or neurodivergent individuals who may struggle with expressing ideas in writing.
AI-enhanced task management
AI-productivity apps like Goblin.tools make task text-driven tasks more manageable. For example, Goblin has a feature called “Judge” that assesses the tone of written text and another feature called “Compiler” that turns a “brain dump” into a list of actionable next steps.
From where we’re at now, it’s almost impossible to understand AI’s full potential to enhance and improve digital accessibility. Conversational chatbots, tools that help us process the tone of speech, automation that frees us from mindless and energy-draining tasks – these provide a glimpse of what’s possible.
It seems that anything is possible. In the next decade we could all have a robot at our disposal to fetch a second cup of coffee, water the plants, and organize our desk. As more businesses embrace AI to enhance workplace accessibility, we inch closer to a world where every employee can thrive, contribute, and connect.
Dig Deeper
Employees expect more from their workplaces. Even before the transition to a hybrid work model brought new challenges to workplace collaboration, workers needed ways to streamline all the information coming at them.
Learn more ways to build an AI-powered employee experience to help you attract, retain, and develop talent in our free ebook, Guide to Delivering AI-Powered Employee Experiences.